Sophia McCarthy
Operations Manager
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a condition that is far more common than many of us realise. In fact, according to womenshealth.gov, the condition “affects 1 in 10 women of childbearing age.”
So what exactly is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome – or, as it’s most often referred to as – PCOS?
What is PCOS?
Most women are born with two ovaries, with each one on either side of the womb (or uterus).
The ovaries are glands that normally measure 2.5-5 cm long, 1.5-3 cm wide, and 0.6-1.5 cm thick; roughly the size of a large marble. Their main job is to make and release eggs for fertilization and to generate estrogen and progesterone; hormones that ensure healthy development during puberty and to assist fertility.
The ovaries can become enlarged for many reasons that are often harmless, such as during your menstrual cycle. Every month, an ovary will develop a slight swell as it forms an ovum (egg). The ovum forms within something called a follicle (a small cyst). The ovary will actually grow several tiny follicles in preparation for ovulation, but only one of these will fully develop an ovum to be released into the fallopian tube. According to the Fertility Family website:
A woman is considered to have adequate or normal ovarian reserve if the antral follicle count is 6-10. If the count is less than 6 the ovarian reserve could be considered to be low, whereas a high reserve is greater than 12.
So what happens when there is a high reserve of follicles that are not ovulating? This means there are several (poly) follicles (cysts) – indicating a possible diagnosis of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
What causes PCOS?
The exact reason as to why PCOS develops is not clear, but there are several interlinking factors that can contribute to the condition, such as:
Insulin resistance
If the cells in the body are not processing insulin properly, insulin is overproduced in an attempt to maintain blood sugar levels. This raised level of insulin in the body can cause the ovaries to produce too much testosterone and can also lead to weight gain.
- Conversely, being overweight can trigger this insulin resistance.
Testosterone
Raised levels of insulin and testosterone can hinder the full development of the follicles, meaning they can form but not release. This raised testosterone can appear in the form of excess hair growth, acne and thinning hair on the scalp.
Luteinising Hormone or LH
This hormone originates from the pituitary gland. LH helps to stimulate the ovaries, teaming up with insulin to increase the production of testosterone. Raised levels can contribute to excess testosterone.
What are some symptoms of PCOS?
It is important to note that not all of the below symptoms may be present if someone is diagnosed with PCOS. They can also vary in severity for each person. These symptoms most often begin to appear for women in their early twenties or late teens:
- Issues with periods: This may present as irregular or light periods, or sometimes no period at all.
- Fertility issues: Due to ovulation not occurring.
- Weight gain
- Hirutism (excessive hair growth): This can appear on the face, chest or lower abdomen.
- Hair thinning on the scalp
How is PCOS diagnosed?
Your doctor may request a blood test for you. This test will measure the amount of certain hormones present in the blood, such as testosterone or LH. You may also be referred for a pelvic ultrasound to examine the ovaries.
What does PCOS look like on an ultrasound?
Normal Ovaries

Above is an ultrasound image of ovaries functioning normally. As you can see, there are a few follicles but not an excess of them, as is expected during a normal cycle. Note that the follicles are also more or less the same in size.
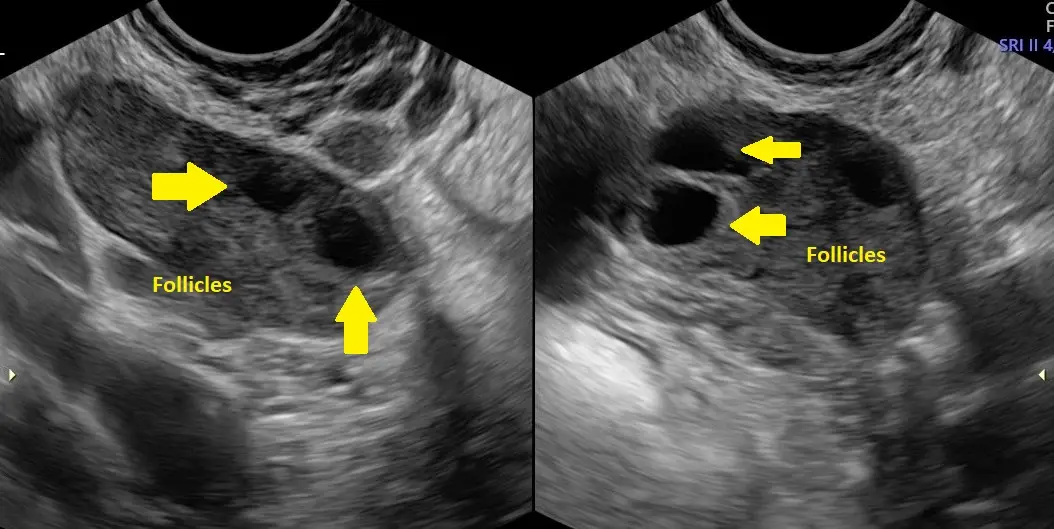
Polycystic Ovaries

The above image is an example of polycystic ovaries. The excess of follicles is quite evident. They also seem to be of varying sizes.
How is PCOS treated?
While there is no cure for the condition, the symptoms that go along with it can be alleviated through a combined approach.
- If you are overweight, losing weight can help to regulate insulin levels, which will in turn reduce testosterone levels.
- Your doctor may suggest insulin reducing drugs, such as Metformin.
- Unwanted hair can be treated through electrolysis and laser treatments.
- Lifestyle changes that can alleviate symptoms include; following a healthy diet, quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol and exercising regularly.
- Fertility treatments may be recommended by a specialist.
You can find out more information about our Pelvic Scan here. If you would like more information on anything covered in this post, you can get in touch via info@theultrasoundsuite.ie or send us a message on our Facebook page and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Our website www.theultrasoundsuite.ie also provides a wealth of information on our various policies and procedures.
We look forward to seeing you soon!